Interactions between magnetosonic waves and radiation belt electrons: Comparisons of quasi-linear calculations with test particle simulations Jinxing Li, Binbin Ni, Zuyin Pu, Jacob Bortnik, Lunjin Chen, Richard. M. Thorne, Qianli Ma, Suiyan Fu, Lun Xie, Xiaogang Wang, Chijie Xiao, Zhonghua Yao, Ruilong Guo
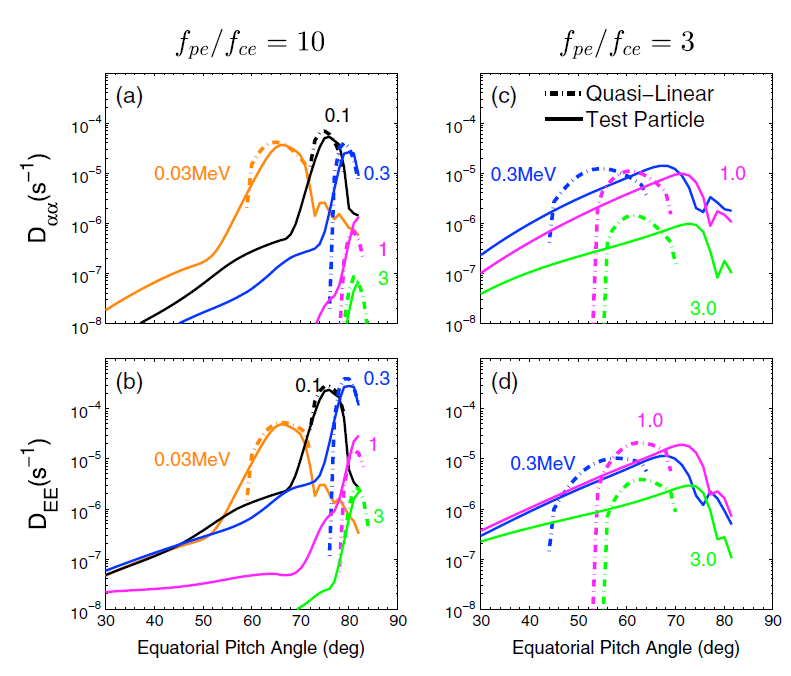
Quasi-linear theory (QLT) has been commonly used to study the Landau resonant interaction between radiation belt electrons and magnetosonic (MS) waves. However, the long-parallel wavelengths of MS waves can exceed their narrow spatial confinement and cause a transit-time effect during interactions with electrons. We perform a careful investigation to validate the applicability of QLT to interactions between MS waves, which have a distribution in frequency and wave normal angle, and radiation belt electrons using test particle simulations. We show agreement between these two methods for scattering rate of intense MS waves at L = 4.5 inside the plasmapause, but find a significant inconsistency for MS waves outside the plasmapause, due to the broad transit-time region in (Ek, PA) space. Consequently, we introduce a particle-independent criterion to justify the validity of QLT for MS waves: the wave spatial confinement should be longer than two parallel wavelengths.
We acknowledge Cluster Active Archive Web sites for provision of data from STAFF instrument on Cluster. This research is supported by the NSFC grants 41374166, 41274167, 41204120, and 40831061 and the Chinese Key Research Project 2011CB811404. UCLA authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the support of NSF’s Geospace Environment Modeling grant AGS-1103064 in performing this work. Binbin Ni also acknowledges the support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities grant 2042014kf0251.
Li, J., et al. (2014), Interactions between magnetosonic waves and radiation belt electrons: Comparisons of quasi-linear calculations with test particle simulations, Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, doi:10.1002/2014GL060461.
